Endocrinology case 4
Endocrinology case 4
Submitted by:
Dr. Harish Goyal
MD DNB FANMB FEBNM MNAMS
Assistant Professor
Department of Nuclear Medicine
AIIMS Raipur, India
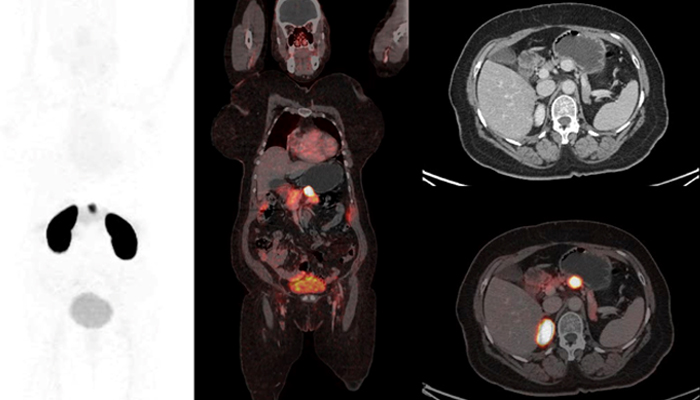
A 35-year-old female with a history of gradually increasing lethargy and multiple episodes of dizziness over the past 6 years underwent a biochemical workup that showed elevated levels of plasma insulin and C-peptide. Patient underwent 68Ga DOTA-Exendin PET/CT imaging. Based on the findings of the scan, what is the most likely explanation for the observed appearance?
A) Nesidioblastosis
B) Insulinoma
C) VIPoma
D) Gastrinoma
Scroll down for answer
Answer: B (Insulinoma)
Discussion:
Insulinomas are the most common neuroendocrine tumors of the pancreas and can occur sporadically or in association with MEN 1 syndrome. They manifest with hypoglycemic symptoms, and elevated plasma insulin and C-peptide levels indicate excessive insulin production. Imaging modalities like contrast-enhanced CT, MRI, and nuclear medicine scans are used to identify and stage insulinomas.
Nuclear medicine techniques for insulinoma imaging include tracers such as 111In-Pentetreotide, 68Ga DOTATATE, 18F-FDOPA, and more recently, glucagon-like-peptide-1 (GLP-1) agents. Although 18F-FDOPA has been commonly used, its limited suitability in adults due to pancreatic uptake affects its tumor detection accuracy. 68Ga DOTA-Exendin PET/CT has emerged as a promising approach for preoperative and intraoperative localization of insulinomas, as they typically express GLP-1 receptors.
In cases of persistent hyperinsulinemic hypoglycemia (PHH) in adults where no identifiable lesion is found, the diagnosis may be nesidioblastosis. Nesidioblastosis involves diffuse proliferation of beta islet cells throughout the pancreas and poses challenges in localization using imaging techniques.
References:
1. Sidrak MMA, De Feo MS, Corica F, et al. Role of Exendin-4 Functional Imaging in Diagnosis of Insulinoma: A Systematic Review. Life (Basel). 2023 Apr 11;13(4):989.
2. Prosperi D, Gentiloni Silveri G, Panzuto F, Faggiano A, et al. Nuclear Medicine and Radiological Imaging of Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Neoplasms: A Multidisciplinary Update. J Clin Med. 2022 Nov 18;11(22):6836.
3. Demartin S, Goffette P, Christ E, et al. Adult-onset nesidioblastosis: a challenging diagnosis revealed by glucagon-like-peptide-1 receptor imaging. Endocrinol Diabetes Metab Case Rep. 2022 Nov 1;2022:22-0325.